Revolutionary Technology Enhances Cell Research
January 23, 2025 - 03:12
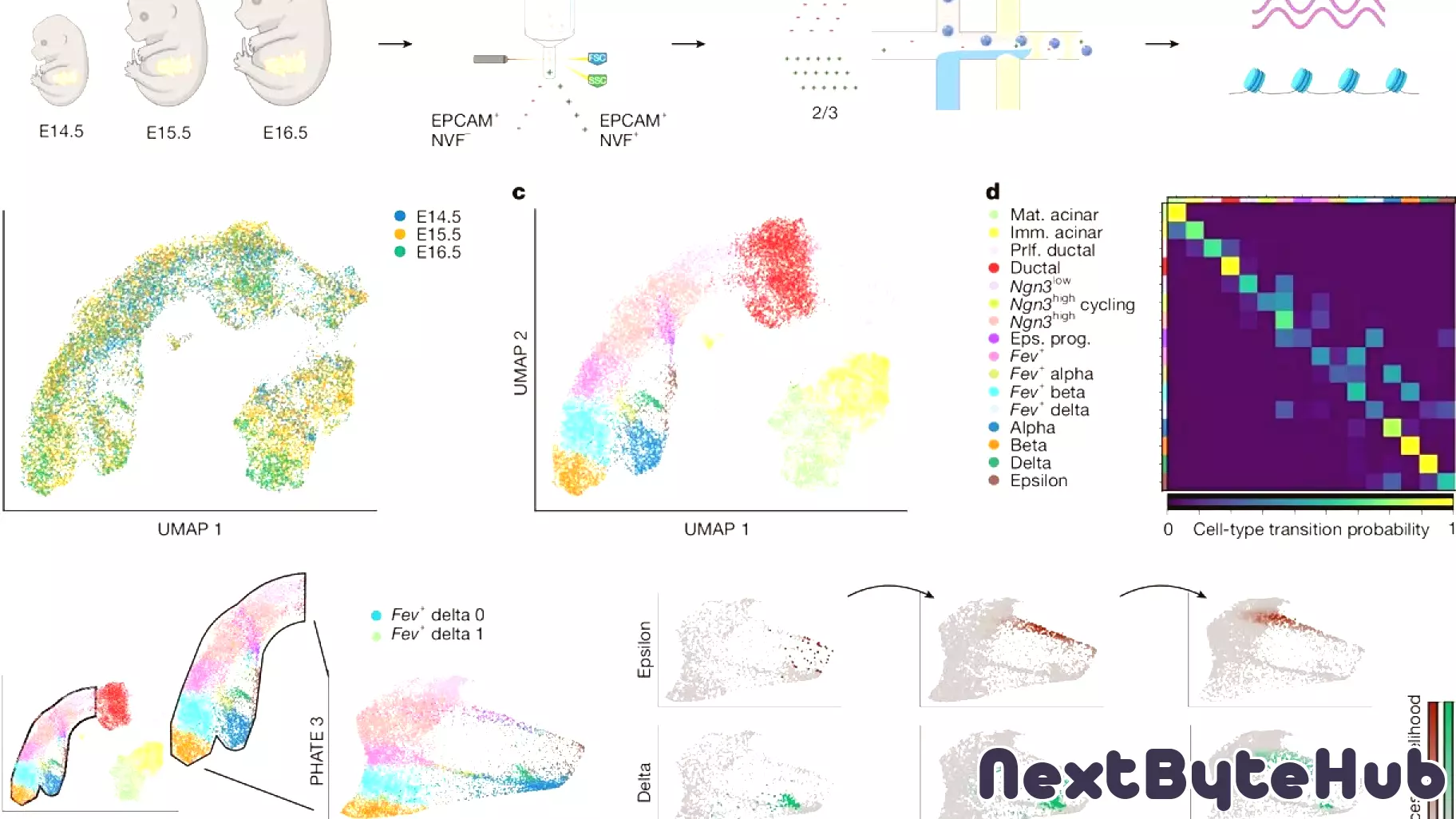
Thanks to a groundbreaking technology known as Moscot ("Multi-Omics Single-Cell Optimal Transport"), researchers are now able to observe millions of cells simultaneously as they progress in their development into new organs, such as the pancreas. This innovative approach offers an unprecedented level of detail in mapping cell dynamics, significantly advancing our understanding of cellular behavior and organogenesis.
Moscot integrates multiple omics data, allowing scientists to track individual cells over time and analyze their interactions and transformations in real-time. This capability not only enhances the resolution of cellular studies but also provides insights into how various cell types contribute to the formation of complex tissues. The implications of this technology extend beyond basic research; it holds the potential to inform regenerative medicine and therapeutic strategies by revealing how to manipulate cell behavior for organ repair and transplantation.
As researchers continue to explore the applications of Moscot, the prospects for breakthroughs in developmental biology and disease treatment are becoming increasingly promising, heralding a new era in cell research.
MORE NEWS

March 2, 2026 - 07:46
Canon: "New Technology" Compact Model is ComingPhotography enthusiasts and industry watchers are abuzz as Canon has released tantalizing hints about a new compact camera model currently in development. While full specifications and an official...

March 1, 2026 - 18:53
Digital Frontiers Reshape Montana's LandscapeThe spirit of innovation that once rode the rails into Montana is finding new expression in the digital age. Across the state, from sprawling ranches to remote mountain towns, modern technology is...
March 1, 2026 - 04:37
Silicon Valley Rallies Behind Anthropic in A.I. Clash With TrumpA significant rift appears to be widening between the federal government and the American technology sector, as industry leaders and workers rally behind artificial intelligence startup Anthropic....

February 28, 2026 - 04:58
Rare Disease Day: Revolutionising clinical trial enrolment and retention with technologyOn Rare Disease Day, the focus sharpens on the unique challenges of developing treatments for conditions affecting small, often geographically dispersed patient populations. A key industry expert...